Ks0193 keyestudio Self-balancing Car: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 267: | Line 267: | ||
=== The UNO Control Board === | === The UNO Control Board === | ||
<br> | |||
When it comes to using the UNO R3 as core of our robot, the UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can start playing with. <br> | |||
[[image:UNO R3--.png|thumb|300px|right]] | |||
<br> | |||
Well, let's at first have a look at this UNO R3 board. | |||
<br>[[Image:UNO.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
{| width="80%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-1.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''USB Connection''' | |||
Arduino board can be powered via USB connector. Or you can program the board via the USB port.<br> | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-2.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''DC Power Jack''' | |||
Arduino board can be supplied with power from the DC power jack | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-3.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Voltage Regulator''' | |||
To control the voltage provided to the Arduino board, as well as to stabilize the DC voltage used by the processor and other components. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-4.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Crystal Oscillator''' | |||
How does Arduino calculate time? by using a crystal oscillator. | |||
The number printed on the top of the Arduino crystal is 16.000H9H. It tells us that the frequency is 16,000,000 Hertz or 16MHz. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-5.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Arduino RESET''' | |||
You can reset your Arduino board, for example, start the program from the very beginning. Firstly, use the RESET button(17). Or you can connect an external reset button to Arduino pin 5 labeled RESET | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-6.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Pin Header(3.3V,5V,GND,Vin''' | |||
[[Image:KS0313 5.1-7.png|500px|frameless]]3.3V - provides 3.3V output voltage <br> | |||
[[Image:KS0313 5.1-8.png|500px|frameless]]5V - provides 5V output voltage<br> | |||
Using 3.3 volts and 5 volts, most components can normally operate with Arduino board together.<br> | |||
[[Image:KS0313 5.1-9.png|500px|frameless]]GND(Ground pins)- two GND headers on Arduino, each of which can be used for circuit ground.<br> | |||
[[Image:KS0313 5.1-10.png|500px|frameless]]Vin - You can supply an external power (like AC power supply) through this pin to Arduino board. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-11.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Analog Pins''' | |||
Arduino UNO board has 6 analog inputs, labeled A0 through A5. These pins can read the signal from analog sensors (such as humidity sensor or temperature sensor), and convert it into the digital value that can read by microcontrollers) | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-12.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Microcontroller ''' | |||
Each Arduino board has its own microcontroller. You can regard it as the brain of your board.<br> | |||
The main IC (integrated circuit) on the Arduino is slightly different from the panel pair. Microcontrollers are usually from ATMEL. Before you load a new program from the Arduino IDE, you must know what IC is on your board. This information can be checked at the top of IC. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-13.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) Header''' | |||
In most case, ICSP is the AVR, an Arduino micro-header consisting of MOSI, MISO, SCK, RESET, VCC, and GND.It is often called the SPI (serial peripheral interface) and can be considered an "extension" of the output.In fact, slave the output devices under the SPI bus host. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-14.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Power LED Indicator''' | |||
Powering the Arduino, LED on means that your circuit board is correctly powered on. If LED is off, connection is wrong. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-15.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''TX and RX LED ''' | |||
Onboard you can find two labels: RX(receive ) and TX (transmit)<br> | |||
First appear on digital pin 0 and 1 for serial communication; <br> | |||
Besides, the RX LED on the board will flash in different speed when serial data is being transmitted. The flash speed depends on the baud rate set by board. And RX LED will also flash during the receiving process. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-16.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Digital I/O''' | |||
Arduino UNO has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs). These pins can be configured as digital input pin to read the logic value (0 or 1). Or used as digital output pin to drive different modules like LED, relay, etc. The pin labeled “〜” can be used to generate PWM. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0313 5.1-17.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''AREF''' | |||
Reference voltage( 0-5V) for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference(). | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br> | |||
=== The Balance Car Shield === | |||
The balance shield is an important part for this balance car. With it, you can DIY the balance car more simple. | |||
It is fully compatible with UNO R3 board; just stack it onto the control board. <br> | |||
The balance shield comes with a 6612FNG chip for driving two DC motors; two white connectors for connecting DC motor; a DC power jack for powering on the shield and UNO R3; <br> | |||
Also comes with a large slide switch for controlling the power switch; a MPU-6050 for testing the posture; a XBEE Bluetooth interface for connecting Bluetooth module to communicate with Andriod devices; a small slide switch for controlling Bluetooth module’s communication; also comes with a button and an active buzzer. <br> | |||
The control pins of UNO R3 are all brought out as female header on the shield; the serial port and I2C communication pins are brought out as pin headers.<br> | |||
<span style=color:red> Note: connect the motor to the motor’s connector on the shield. </span> <br> | |||
'''PINOUT:''' | |||
<br> | |||
===Installing Arduino IDE=== | |||
When you get the UNO development board, first you should install the software and driver of Arduino. You can see all the Arduino software versions from the link below: <br> | |||
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/OldSoftwareReleases#1.5.x <br> | |||
Or you can browse the ARDUINO website at this link, https://www.arduino.cc, pop up the following interface. | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0313-1.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Then click the SOFTWARE on the browse bar, you will have two options ONLINE TOOLS and DOWNLOADS. | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0313-2.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Click DOWNLOADS, it will appear the latest software version of ARDUINO 1.8.5 shown as below. | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0313-3.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
In this software page, on the right side you can see the version of development software for different operating systems. So ARDUINO has a rather powerful compatibility. You should download the software that is compatible with the operating system of your computer.<br> | |||
In our project, we will take WINDOWS system as an example here. There are also two options under Windows system, one is installed version, the other is non-installed version. | |||
For simple installed version, first click Windows Installer, you will get the following page.<br> | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0313-4.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0313-5.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
This way you just need to click JUST DOWNLOAD, then click the downloaded file to install it. <br> | |||
For non-installed version, first click Windows ZIP file, you will also get the pop-up interface as the above figure.<br> | |||
Click JUST DOWNLOAD, and when the ZIP file is downloaded well to your computer, you can directly unzip the file and then click the icon of ARDUINO program to start it. <br> | |||
<br> | |||
===Installing Arduino (Windows)=== | |||
Install Arduino with the exe. Installation package | |||
<br>[[File:Arduino Setup 1.jpg|800px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Click“I Agree”to see the following interface. | |||
<br>[[File:Arduino Setup 2.jpg|800px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Click “Next”. Pop up the interface below. | |||
<br>[[File:Arduino Setup 3.jpg|800px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
You can press Browse… to choose an installation path or directly type in the directory you want.<br> | |||
Then click “Install” to initiate installation. | |||
<br>[[File:Arduino Setup 4.jpg|800px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Wait for the installing process, if appear the interface of Window Security, just continue to click Install to finish the installation. | |||
<br>[[File:Arduino1.5.6- setup 5.png|800px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
All right, up to now, you have completed the Arduino setup! The following icon will appear on your PC desktop. | |||
<br>[[Image:Ks0313图片1.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
Double-click the icon of Arduino to enter the desired development environment shown as below. | |||
<br>[[Image:717.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
===Installing Driver=== | |||
Next, we will introduce the driver installation of UNO R3 development board. The driver installation may have slight differences in different computer systems. So in the following let’s move on to the driver installation in the WIN 7 system. <br> | |||
The Arduino folder contains both the Arduino program itself and the drivers that allow the Arduino to be connected to your computer by a USB cable. Before we launch the Arduino software, you are going to install the USB drivers.<br> | |||
Plug one end of your USB cable into the Arduino and the other into a USB socket on your computer.<br> | |||
When you connect UNO board to your computer at the first time, right click the icon of your “Computer” —>for “Properties”—> click the “Device manager”, under “Other Devices”, you should see an icon for“Unknown device” with a little yellow warning triangle next to it. This is your Arduino.<br> | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 1.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
Then right-click on the device and select the top menu option (Update Driver Software...) shown as the figure below.. | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 2.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
It will then be prompted to either “Search Automatically for updated driversoftware” or “Browse my computer for driver software”. Shown as below. In this page, select “Browse my computer for driver software”. | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 3.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
After that, select the option to browseand navigate to the “drivers” folder of Arduino installation. | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0286-4.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
Click “Next” and you may get a security warning, if so, allow the software to be installed. Shown as below. | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 5.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
Once the software has been installed, you will get a confirmation message. Installation completed, click “Close”. | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 6.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
Up to now, the driver is installed well. Then you can right click “Computer” —>“Properties”—>“Device manager”, you should see the device as the figure shown below. | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 7.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
=== Example Use of ARDUINO IDE === | |||
'''STEP 1: Open Arduino'''<br> | |||
In the previous, we have introduced the driver installation of UNO R3 development board. So this time let’s first have basic understanding of the development environment of ARDUINO. After that, you will learn how to upload the program to Arduino board. <br> | |||
First of all, open the unzipped folder of ARDUINO development software and click icon of ARDUINO to open the software, as the figure shown below. | |||
<br>[[Image:Arduino folder.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
'''STEP 2: Build Projects'''<br> | |||
When open the Arduino software, you will have two options as below:<br> | |||
*Build a new project<br> | |||
*Open an exiting project example <br> | |||
If you want to build a new project, please select “File”→then click “New”, you will see the software interface as follows.<br> | |||
<br>[[Image:Arduino 1-8-5 new.png|400px|frameless]][[Image:0313 箭头.png|500px|frameless]][[Image:Arduino 1-8-5 new2.png|400px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
If you want to open an example project, please select File→Example→Basics→Blink. Shown below.<br> | |||
<br>[[Image:Arduino 1-8-5 example.png|450px|frameless]] [[Image:0313 箭头.png|500px|frameless]][[Image:Arduino 1-8-5 example2.png|400px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
'''STEP 3: Select Arduino Board'''<br> | |||
On the Arduino software, you should click Tools→Board , select the correct board. Here in our tutorial we should select Arduino Uno. Shown as below. | |||
<br>[[Image:Arduino 1-8-5 board.png|500px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
'''STEP 4: Select Serial Port'''<br> | |||
If you are not sure which port is correct, at first directly open the Control Panel of your computer, then click to open Device Manager, you can check the COM port here. Shown as below. <br> | |||
<br>[[Image:Driver 7.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Then you should click Tools→Serial Port. It may be COM3 or higher (COM1 and COM2 are usually reserved as hardware serial port). | |||
<br>[[Image:Arduino 1-8-5 port.png|500px|frameless]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
'''STEP 5: Upload the Code to Your Board'''<br> | |||
Before showing you how to upload the code to your board, first of all let me introduce the function of each icon on the Tool bar of Arduino IDE. Look at the picture showed below. | |||
<br>[[Image:图片1- arduino toolbar.png|500px|frameless]]<br> | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | |||
|- | |||
!scope="row" |[[Image:IDE 1.png|600px|frameless]] Verify/Compile | |||
| Check the code for errors | |||
|- | |||
!scope="row" |[[Image:IDE 2.png|600px|frameless]] Upload | |||
| Upload the current Sketch to the Arduino | |||
|- | |||
!scope="row" |[[Image:IDE 3.png|600px|frameless]] New | |||
| Create a new blank Sketch | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" |[[Image:IDE 4.png|600px|frameless]] Open | |||
| Show a list of Sketches | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" |[[Image:IDE 5.png|600px|frameless]] Save | |||
| Save the current Sketch | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" |[[Image:IDE 6.png|600px|frameless]] Serial Monitor | |||
| Display the serial data being sent from the Arduino | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Revision as of 15:40, 25 April 2019
Overview
How to DIY a mini balance car on your own? This balance car kit is based on Arduino development platform. We mainly use UNO R3 as core and balance shield with built-in MPU-6050 as drive board to test the car body posture.
The balance shield comes with a Bluetooth interface, fully compatible with the Bluetooth XBee module (only compatible with Andriod system).
When connecting to Bluetooth, you can easily control the moving direction of balance car with Bluetooth APP, making a variety of unique postures.
To facilitate the operation control, Bluetooth APP has both key and gravity control modes.
Moreover, it adds the function of adjusting the balance angle and PID parameters as well, so you can perfectly adjust and control the balance car.
No need to worry how to play it. We can provide you with all assembly components, as well as the corresponding installation, debugging method and program.
Operation Principle
The self-balancing car uses the power of the car body to maintain the relative balance, which is a process of dynamic balance.
The power to maintain the balance of the car comes from the movement of the wheels, driven by two DC motors.
The control of the car body can be divided into three control tasks as follows:
- 1. Balance Control: keep the car upright and balanced by controlling the forward and backward rotation of the car’s wheel.
- 2. Speed Control: realize the front and rear movement and speed control by controlling the inclination of the car. In fact, it is achieved finally by controlling the speed of the motor.
- 3. Direction Control: realize the steering control by controlling the rotational speed differences between the two motors of the car.
In this way, it is relatively simple to understand the three control tasks.
But in the final control process, it comes down to the control of a control quantity. So there will be coupling between the three tasks, which will interfere with each other.
The key is to control the car’s balance; the speed and direction control should be as smooth as possible.
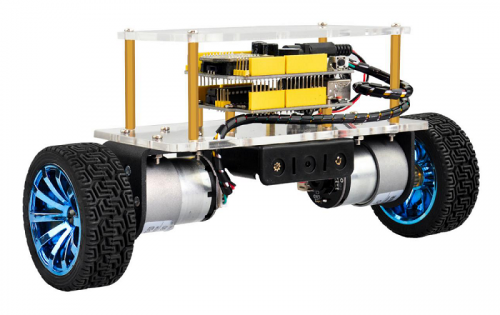
Parameters of balance car
- 1.Motor parameters:
- 2.Working voltage: DC 9-12V
- 3.Motor drive chip: TB6612FNG
- 4.Body posture detection: MPU-6050
- 5.Comes with power control switch
- 6.Comes with Bluetooth control switch for controlling serial communication
Pay special attention to:
The balance shield comes with a slide switch for controlling the Bluetooth communication.
When upload the source code, must turn the slide switch OFF; otherwise, code uploading will fail.
When connecting to the Bluetooth module, should turn the slide switch ON.
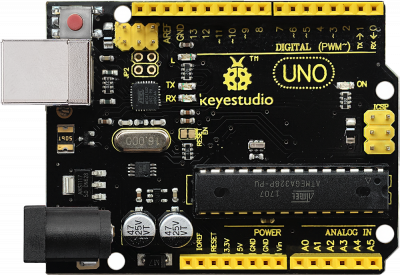
Kit List
The kit packaging contains all electronic components for this self-balancing car. As you work your way through each project, you will learn how to control the car.
Assembly Steps
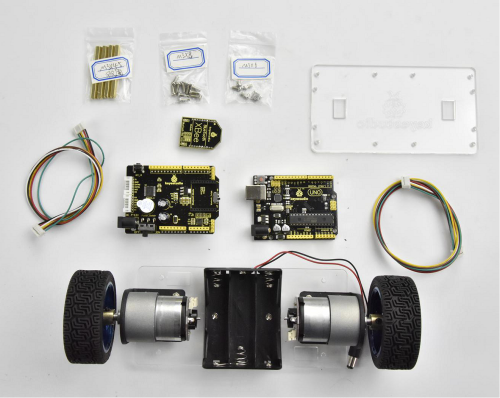
(1) Prepare all the components shown below.

(2) To begin with, we start to install the bottom Acrylic plate.
Find out the parts below:
- Bottom Acrylic plate
- Dual-pass M3*10MM hex copper pillar x 4pcs
- M3*8MM screw x 4pcs
- M3*12MM flat head screw x 2pcs
- M3 nickel plating nut x 2pcs
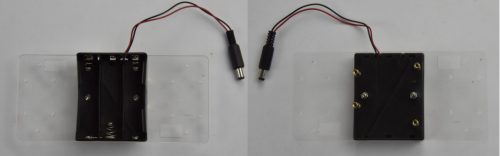
- Battery case
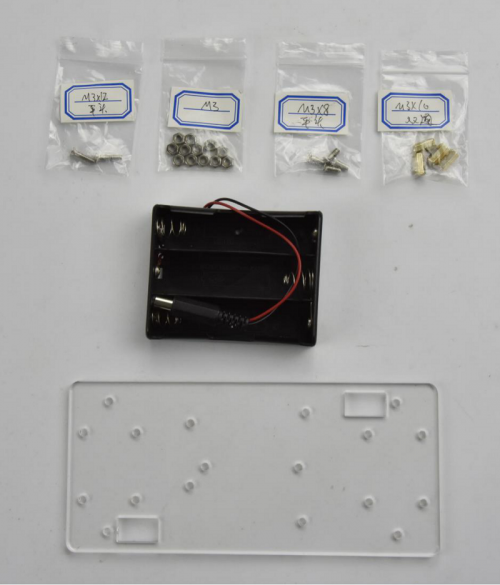

We are now going to mount the battery case and copper pillars on the Acrylic plate.
Fix the 4pcs M3*10MM copper pillar onto the Acrylic plate using 4pcs M3*8MM screws.

Then Mount the battery case on the Acrylic plate using 2pcs M3*12MM flat head screws and 2pcs M3 nickel plating Nuts.
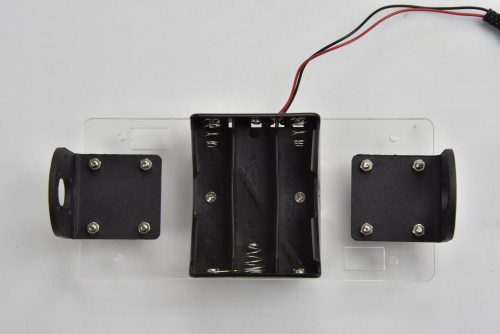
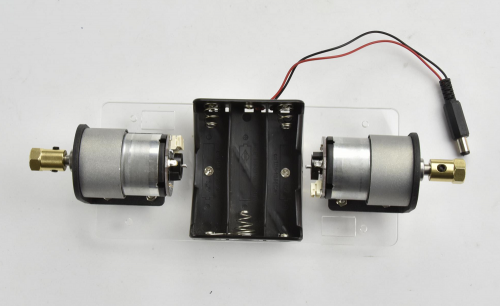
(3) Next, move on to install the motor and wheel onto bottom Acrylic plate.
Find out the parts below:
- Bottom Acrylic plate mounted with battery case
- M3*12MM round-head screw x 8pcs
- M3 nickel plating nut x 8pcs
- M4*6MM black screw x 2pcs
- Two wheels
- Two black connectors
- Two motors
- Two copper hex couplers
- M2 wrench Type L

Go to mount the two black connectors onto the Acrylic plate using 8pcs M3*12MM round-head screws and 8pcs M3 nickel plating nuts. Shown below.
Each motor is equipped with six screws in the bag. Go to mount the two motors on the black connectors using the screws.

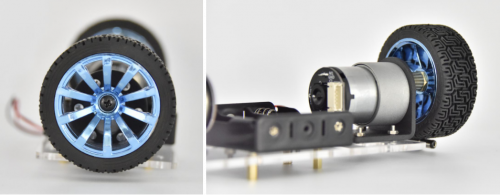
Screw each copper hex couplers with two screws. Then fix the two copper couplers on the two motors using a wrench.
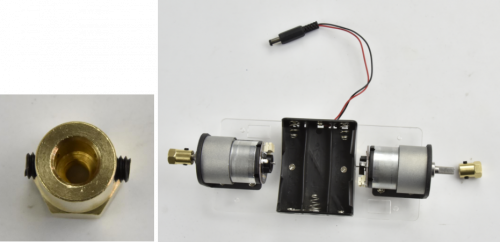
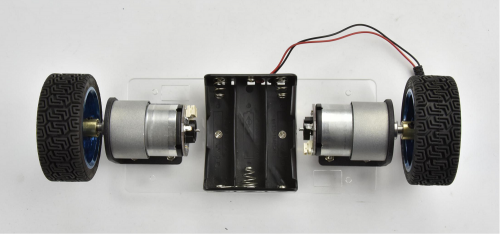
Finally mount the two wheels to the two hex copper couplers using 2pcs M4*6MM black screws.
Up to now, the bottom motor wheel are installed well!
(4) The final step is to install the control board and the top Acrylic plate.
- Top Acrylic plate
- UNO R3 control board
- keyestudio balance shield
- Bluetooth XBee module HC-06
- M3*6MM round-head screw x 3pcs
- M3*45MM copper pillar x 4pcs
- M3*8MM round-head screw x 8pcs
- 6pin 30CM connector wire x 2pcs
Go to screw the UNO R3 control board onto the 4pcs M3*10MM copper pillars mounted on the Acrylic plate with 3pcs M3*6MM round-head screws.
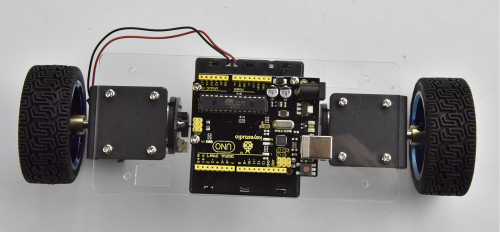
Then stack the keyestudio balance shield onto UNO R3 control board. And plug the Bluetooth XBee module HC-06 into the balance shield.
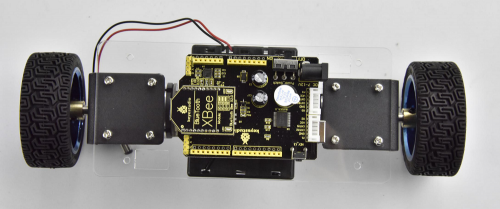
Go to connect the motor to the balance shield using 6pin PH2.0 30CM connector wire. Simply connect the motor to the nearest motor connector.
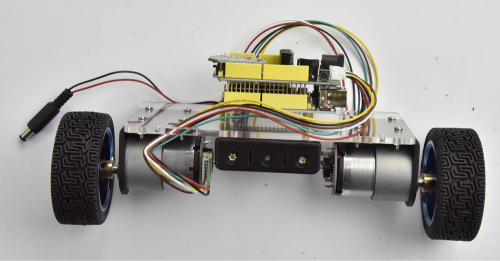
After that, screw the 4pcs M3*45MM copper pillars on the Acrylic plate with 4pcs M3*8MM round head screws. And connect well the battery plug to DC black jack of UNO R3.
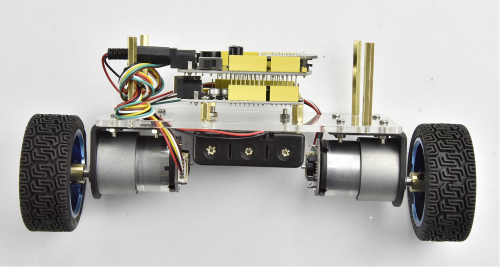
The back view is showed below:

The final part is to install the top Acrylic plate onto the 4pcs M3*45MM copper pillars with 4pcs M3*8MM round-head screws.

Congrats! The balance car is installed well.
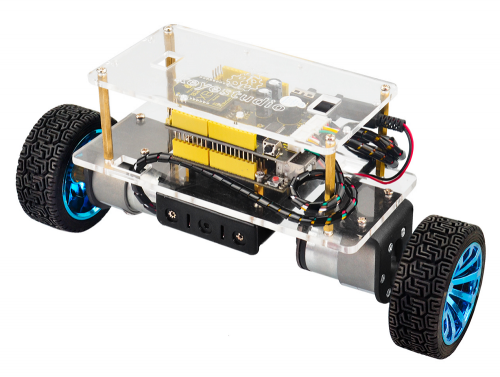
Project 1: Getting Started with Main Board and ARDUINO
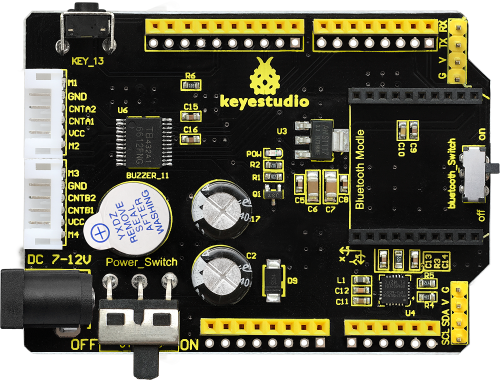
The UNO Control Board
When it comes to using the UNO R3 as core of our robot, the UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can start playing with.
Well, let's at first have a look at this UNO R3 board.

The Balance Car Shield
The balance shield is an important part for this balance car. With it, you can DIY the balance car more simple.
It is fully compatible with UNO R3 board; just stack it onto the control board.
The balance shield comes with a 6612FNG chip for driving two DC motors; two white connectors for connecting DC motor; a DC power jack for powering on the shield and UNO R3;
Also comes with a large slide switch for controlling the power switch; a MPU-6050 for testing the posture; a XBEE Bluetooth interface for connecting Bluetooth module to communicate with Andriod devices; a small slide switch for controlling Bluetooth module’s communication; also comes with a button and an active buzzer.
The control pins of UNO R3 are all brought out as female header on the shield; the serial port and I2C communication pins are brought out as pin headers.
Note: connect the motor to the motor’s connector on the shield.
PINOUT:
Installing Arduino IDE
When you get the UNO development board, first you should install the software and driver of Arduino. You can see all the Arduino software versions from the link below:
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/OldSoftwareReleases#1.5.x
Or you can browse the ARDUINO website at this link, https://www.arduino.cc, pop up the following interface.

Then click the SOFTWARE on the browse bar, you will have two options ONLINE TOOLS and DOWNLOADS.

Click DOWNLOADS, it will appear the latest software version of ARDUINO 1.8.5 shown as below.

In this software page, on the right side you can see the version of development software for different operating systems. So ARDUINO has a rather powerful compatibility. You should download the software that is compatible with the operating system of your computer.
In our project, we will take WINDOWS system as an example here. There are also two options under Windows system, one is installed version, the other is non-installed version.
For simple installed version, first click Windows Installer, you will get the following page.

This way you just need to click JUST DOWNLOAD, then click the downloaded file to install it.
For non-installed version, first click Windows ZIP file, you will also get the pop-up interface as the above figure.
Click JUST DOWNLOAD, and when the ZIP file is downloaded well to your computer, you can directly unzip the file and then click the icon of ARDUINO program to start it.
Installing Arduino (Windows)
Install Arduino with the exe. Installation package
Click“I Agree”to see the following interface.
Click “Next”. Pop up the interface below.
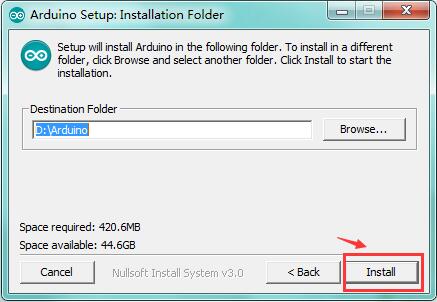
You can press Browse… to choose an installation path or directly type in the directory you want.
Then click “Install” to initiate installation.
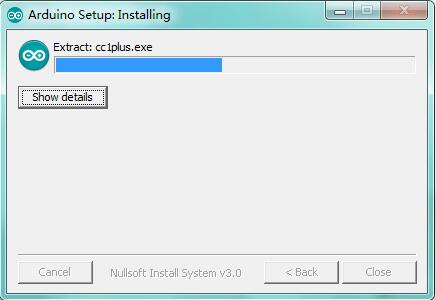
Wait for the installing process, if appear the interface of Window Security, just continue to click Install to finish the installation.
All right, up to now, you have completed the Arduino setup! The following icon will appear on your PC desktop.

Double-click the icon of Arduino to enter the desired development environment shown as below.
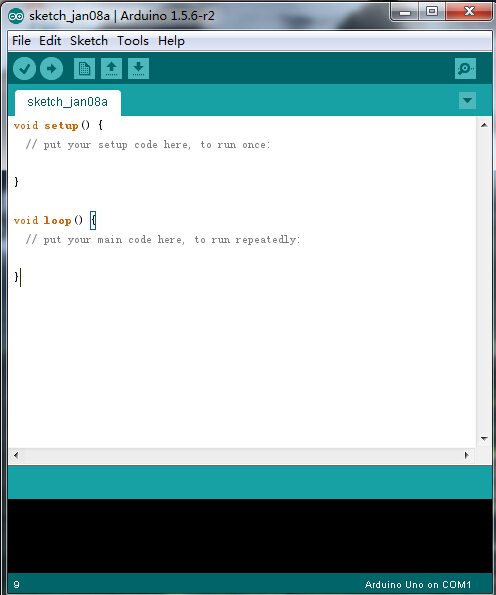
Installing Driver
Next, we will introduce the driver installation of UNO R3 development board. The driver installation may have slight differences in different computer systems. So in the following let’s move on to the driver installation in the WIN 7 system.
The Arduino folder contains both the Arduino program itself and the drivers that allow the Arduino to be connected to your computer by a USB cable. Before we launch the Arduino software, you are going to install the USB drivers.
Plug one end of your USB cable into the Arduino and the other into a USB socket on your computer.
When you connect UNO board to your computer at the first time, right click the icon of your “Computer” —>for “Properties”—> click the “Device manager”, under “Other Devices”, you should see an icon for“Unknown device” with a little yellow warning triangle next to it. This is your Arduino.
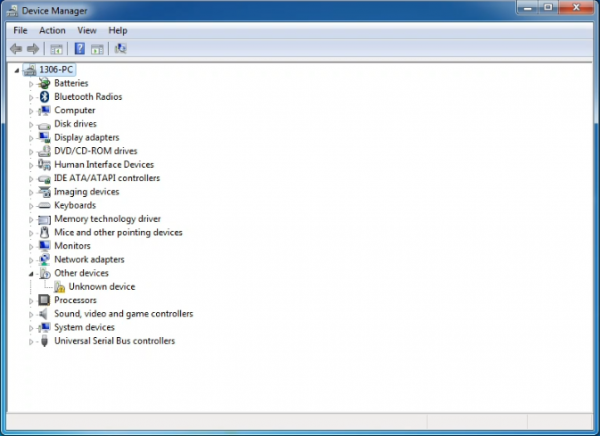
Then right-click on the device and select the top menu option (Update Driver Software...) shown as the figure below..
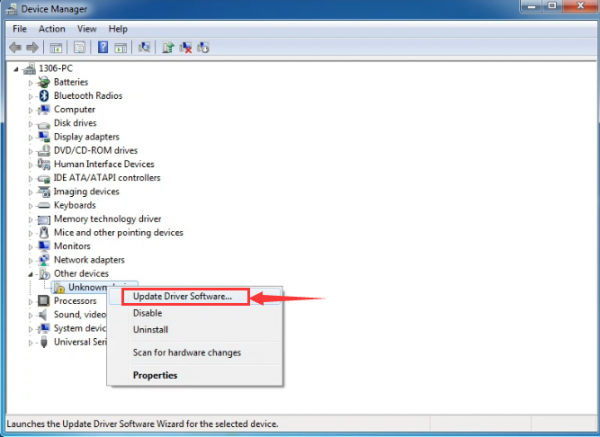
It will then be prompted to either “Search Automatically for updated driversoftware” or “Browse my computer for driver software”. Shown as below. In this page, select “Browse my computer for driver software”.
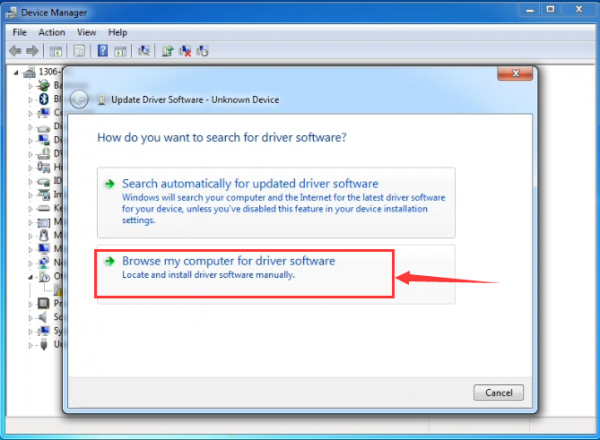
After that, select the option to browseand navigate to the “drivers” folder of Arduino installation.
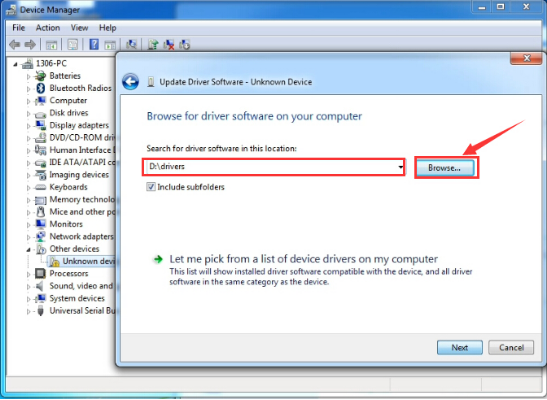
Click “Next” and you may get a security warning, if so, allow the software to be installed. Shown as below.
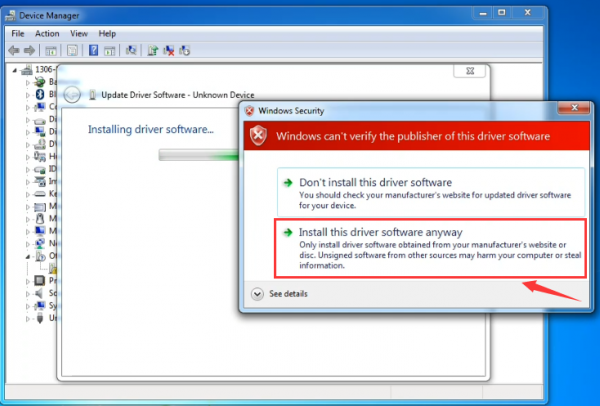
Once the software has been installed, you will get a confirmation message. Installation completed, click “Close”.
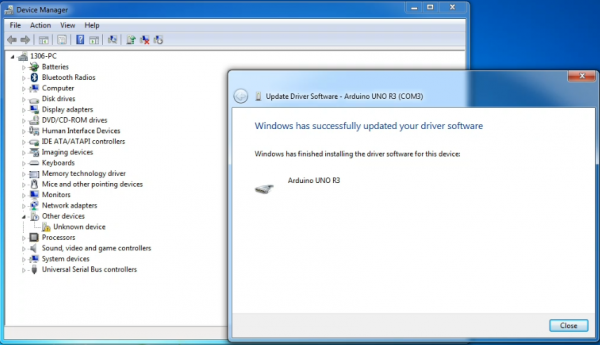
Up to now, the driver is installed well. Then you can right click “Computer” —>“Properties”—>“Device manager”, you should see the device as the figure shown below.
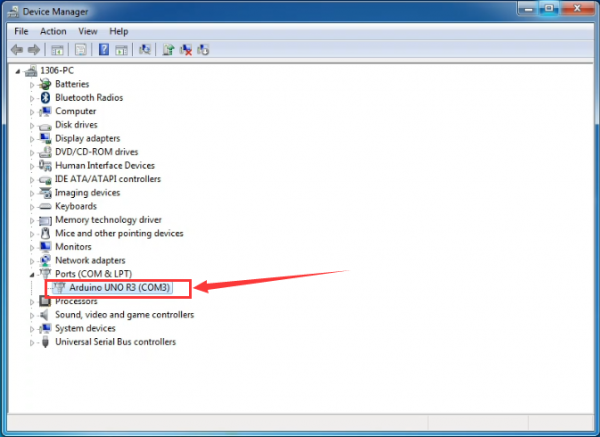
Example Use of ARDUINO IDE
STEP 1: Open Arduino
In the previous, we have introduced the driver installation of UNO R3 development board. So this time let’s first have basic understanding of the development environment of ARDUINO. After that, you will learn how to upload the program to Arduino board.
First of all, open the unzipped folder of ARDUINO development software and click icon of ARDUINO to open the software, as the figure shown below.
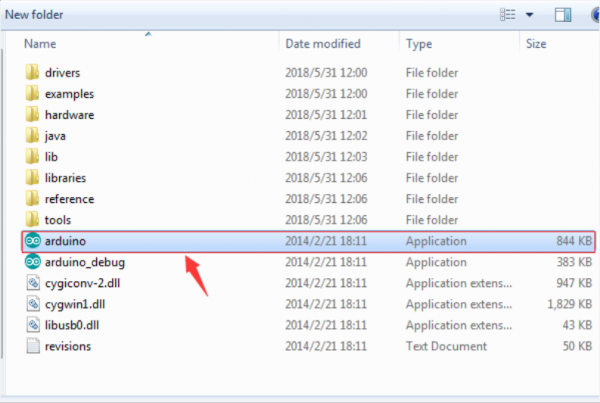
STEP 2: Build Projects
When open the Arduino software, you will have two options as below:
- Build a new project
- Open an exiting project example
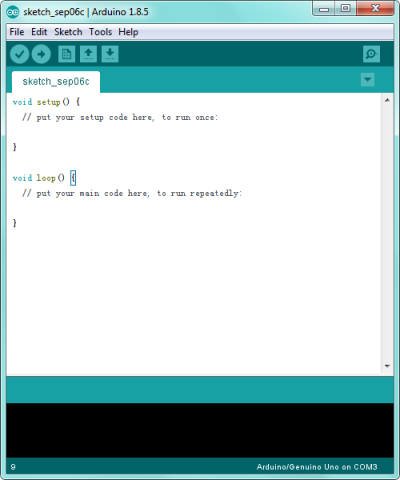
If you want to build a new project, please select “File”→then click “New”, you will see the software interface as follows.
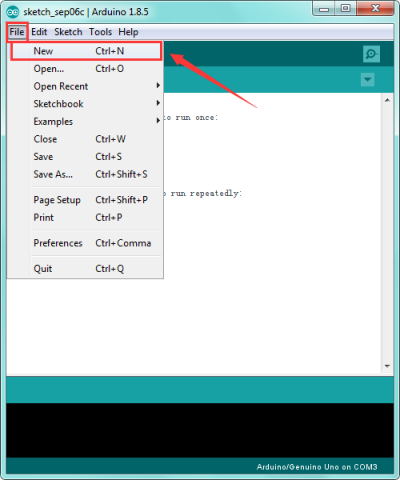
![]()
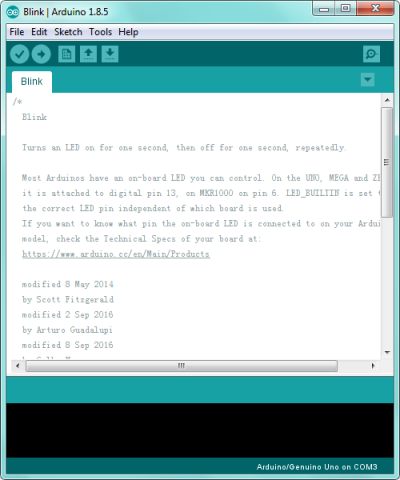
If you want to open an example project, please select File→Example→Basics→Blink. Shown below.
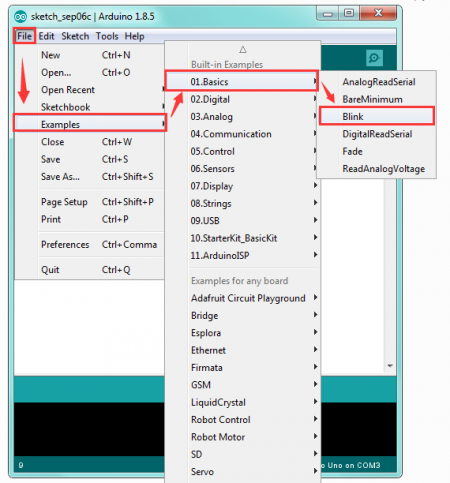
![]()
STEP 3: Select Arduino Board
On the Arduino software, you should click Tools→Board , select the correct board. Here in our tutorial we should select Arduino Uno. Shown as below.
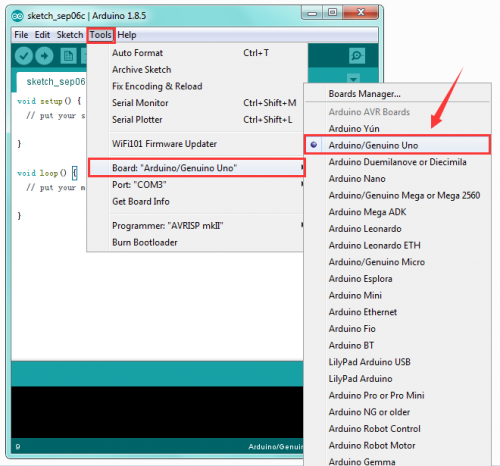
STEP 4: Select Serial Port
If you are not sure which port is correct, at first directly open the Control Panel of your computer, then click to open Device Manager, you can check the COM port here. Shown as below.

Then you should click Tools→Serial Port. It may be COM3 or higher (COM1 and COM2 are usually reserved as hardware serial port).
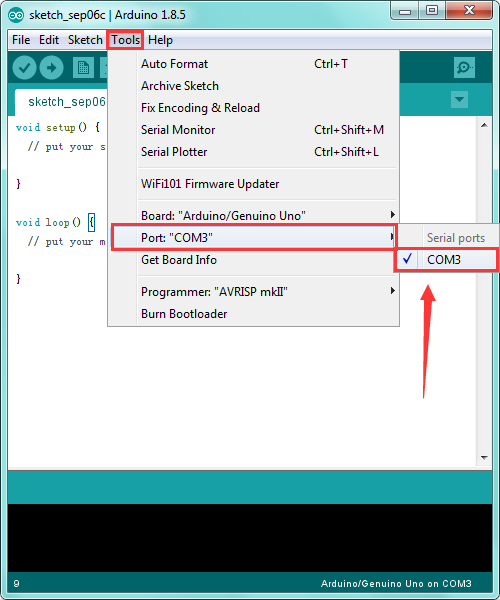
STEP 5: Upload the Code to Your Board
Before showing you how to upload the code to your board, first of all let me introduce the function of each icon on the Tool bar of Arduino IDE. Look at the picture showed below.
![]()